ferment black garlic technology-how to make black garlic
Black Garlic Production Process (Fermentation Technology)
Black garlic is produced by fermenting fresh garlic under high temperature and humidity conditions for an extended period. The production process consists of the following key steps:
1. Garlic Selection
- Select fresh, plump, disease-free garlic (single-clove garlic is preferred for more uniform fermentation)
- Clean the garlic thoroughly to remove dirt and impurities, then air-dry

2. Fermentation (Key Process) of black garlic
- Temperature control: Typically maintained at 60-80°C (may vary slightly depending on specific processes)
- Humidity control: Maintained at 80-90% to prevent dehydration
- Fermentation duration: Usually 30-90 days (longer fermentation results in softer texture and sweeter taste)
- Anaerobic environment: Some processes use sealed fermentation (e.g., vacuum packaging) to reduce oxidation and promote Maillard reaction and enzymatic action
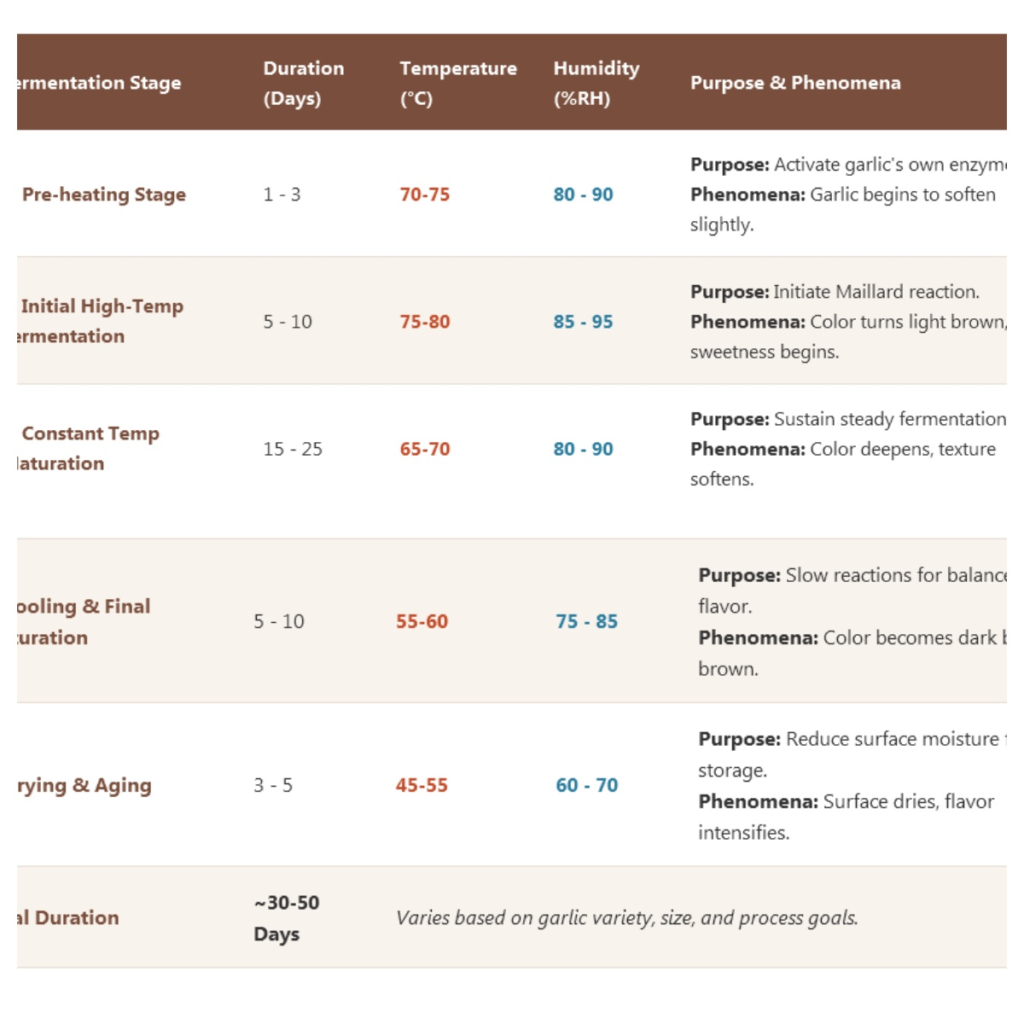
3. Aging and Drying
- After fermentation, the black garlic becomes soft and turns dark brown to black
- Some processes include brief low-temperature drying to adjust moisture content and texture
4. Final Packaging
- Black garlic can be consumed directly or vacuum-packed for extended shelf life
Flavor and Nutritional Changes in Black Garlic
- Taste: Transforms from pungent to sweet and soft (reduction in allicin, increase in reducing sugars during fermentation)
- Color: Turns dark brown/black due to Maillard reaction (non-enzymatic browning)
- Nutritional value: Increased antioxidant content (e.g., S-allyl cysteine) with better bioavailability

Common Production Methods of black garlic
- Traditional fermentation: Natural temperature/humidity control, longer fermentation (60-90 days)
- Modern controlled fermentation: Uses specialized equipment (e.g., black garlic fermentation chambers), reduces time to ~30 days
- Vacuum fermentation: Garlic is vacuum-sealed before fermentation, resulting in purer flavor
Vacuum Fermentation Method for Black Garlic
Vacuum fermentation is a modern black garlic production technique where garlic is fermented in a vacuum-sealed environment with controlled temperature and humidity. This method reduces oxidation, accelerates fermentation, and improves product quality and flavor.
1. Core Principles of Vacuum Fermentation
- Oxygen isolation: Vacuum environment (typically -0.08~-0.1MPa) inhibits aerobic microorganisms and reduces oxidation while promoting anaerobic fermentation
- Optimized Maillard reaction: In low-oxygen conditions, sugars and amino acids in garlic undergo Maillard reaction more efficiently, developing the characteristic dark color, sweetness, and soft texture
- Preservation of volatile compounds: Reduces loss of sulfur compounds (e.g., allicin), resulting in milder flavor
2. Vacuum Fermentation Process Flow
(1) Pre-treatment
- Garlic selection: Choose fresh, plump garlic (single-clove preferred), clean and air-dry
- Vacuum packaging: Pack whole bulbs or peeled cloves in heat-resistant vacuum bags and seal under vacuum
(2) Fermentation Stage
- Temperature control: 60-80°C (may vary by specific process)
- Humidity control: Self-contained moisture in bags (vacuum sealing prevents dehydration)
- Fermentation time: Typically 20-40 days (1/3 shorter than traditional methods)
(3) Aging and Drying
- After fermentation, black garlic turns dark brown with soft texture
- Optional brief low-temperature drying (~50°C) to adjust moisture and prevent excessive stickiness
(4) Final Packaging
- Sold in original vacuum packaging or sterilized and repackaged
3. Vacuum Fermentation vs Traditional Fermentation
| Comparison Item | Vacuum Fermentation | Traditional Fermentation |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen exposure | Anaerobic environment, less oxidation | Aerobic environment, possible partial oxidation |
| Fermentation time | 20-40 days (faster) | 60-90 days (slower) |
| Flavor | Sweeter, milder, less sulfurous | May retain some pungency |
| Color uniformity | More consistent dark brown | Possible uneven coloration |
| Equipment requirements | Vacuum packager, temperature-controlled chamber | Only requires high-temperature/humidity environment (e.g., fermentation room) |
4. Advantages of Vacuum Fermentation
- ✅ High efficiency: Shorter fermentation time suitable for industrial production
- ✅ Consistent quality: More uniform color/texture, less prone to mold
- ✅ Superior flavor: Prominent sweetness without harsh sulfur notes
- ✅ Nutrient preservation: Less loss of antioxidants (e.g., polyphenols, S-allyl cysteine)
5. Applications of black garlic
- Industrial production: Food manufacturers, health supplement companies
- Premium black garlic products: Ready-to-eat black garlic, black garlic extracts
- Research applications: For optimizing fermentation parameters (temperature, duration, etc.)
Vacuum Fermentation——-whats that?
Vacuum Fermentation Method for Black Garlic Production
1. Introduction to Vacuum Fermentation for black garlic
Vacuum fermentation is an advanced technological process for producing that involves fermenting garlic in an oxygen-free environment under controlled temperature and humidity conditions. This method significantly enhances the fermentation efficiency and product quality compared to traditional methods.
2. Core Principles
- Anaerobic Environment: Maintains oxygen levels below 0.5% through vacuum sealing (-0.08~-0.1MPa)
- Enhanced Maillard Reaction: Promotes optimal conditions for sugar-amine reactions at 60-80°C
- Moisture Retention: Prevents dehydration through sealed packaging
- Microbial Control: Inhibits aerobic bacteria while promoting beneficial enzymatic activity
3. Production Process Flow
3.1 Raw Material Preparation
- Selection of premium quality garlic (single-clove preferred)
- Cleaning and surface sterilization
- Moisture content adjustment to 60-65%
3.2 Vacuum Packaging of black garlic
- Use of high-barrier vacuum bags (PET/AL/PE composite material)
- Vacuum degree: -0.095±0.005MPa
- Sealing temperature: 180-200°C
3.3 Primary Fermentation
- Temperature: 70±2°C
- Duration: 15-20 days
- No humidity control required (self-contained in package)
3.4 Secondary Fermentation
- Temperature: 65±2°C
- Duration: 10-15 days
- Color development and flavor maturation
3.5 Post-Processing
- Cooling to room temperature
- Optional drying (50°C for 4-6 hours if needed)
- Quality inspection and packaging
4. Technical Advantages
- ✓ 40-50% faster than traditional fermentation methods
- ✓ Energy saving: 30% less energy consumption
- ✓ Higher yield: 95%+ success rate compared to 80-85% with traditional methods
- ✓ Superior product quality: More consistent color, texture and flavor
- ✓ Extended shelf life: 12-18 months without preservatives
5. Equipment Requirements for black garlic
- Vacuum packaging machine: Dual-chamber type with 90×60cm working area
- Fermentation chambers: Temperature accuracy ±0.5°C, capacity 500-1000kg/batch
- Control system: PLC with temperature programming and data logging
- Auxiliary equipment: Cleaning system, drying oven, inspection table
| Parameter | Vacuum Fermentation | Traditional Fermentation |
|---|---|---|
| Total Process Time | 25-35 days | 60-90 days |
| Temperature Control | ±1°C precision | ±5°C variation |
| Product Consistency | 95% uniformity | 70-80% uniformity |
| Production Capacity | 3-4 batches/month | 1-1.5 batches/month |
| Labor Requirement | 30% less | Higher manpower needed |
6. Quality Specifications for black garlic
- Appearance: Uniform black color, no white spots
- Texture: Soft and elastic, 60-65% moisture content
- Flavor: Sweet with slight acidity, no bitter aftertaste
- Nutrition: S-allyl cysteine ≥0.8mg/g, polyphenols ≥5mg/g
- Microbiology: Total plate count ≤1000CFU/g, no pathogens
7. Commercial Applications of black garlic
- Food industry: Snacks, ingredients, functional foods
- Health products: extracts, supplements
- Culinary uses: High-end restaurants, gourmet products
- Export products: Meeting international food standards
Black Garlic in Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Black Garlic Fermentation Machines
Is Magical Black Garlic Worth Buying
ferment black garlic technology-how to make black garlic
Moisture on Black Garlic Fermentation